Obesity arises from an imbalance of calorie intake and expenditure, leading to various health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and joint problems. Understanding its multifaceted causes and implementing preventive measures are vital for mitigating its effects.
Obesity, a widespread and growing concern, has its roots in genetic predispositions, unhealthy dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, and even psychological factors. It poses a significant threat to individual health, increasing the risk of various chronic diseases and reducing overall quality of life.
The rise in obesity rates globally calls for immediate attention and action. Society must address the underlying factors contributing to this health crisis by promoting balanced diets, physical activity, and increased public awareness. The introduction of comprehensive education programs focusing on nutrition and lifestyle choices can empower individuals to make healthier decisions. Given the complex nature of this condition, a multi-pronged approach involving healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities is necessary to curb the epidemic of obesity. The need to create environments that support healthier lifestyle choices has never been more critical, as they play a pivotal role in the prevention and management of obesity.
Obesity Unpacked: A Modern Health Crisis
Obesity is a complex health issue facing millions worldwide. It impacts physical, psychological, and social well-being. This section delves into the heart of obesity as a modern health crisis, exploring its growing presence and multidimensional definition.
The Rising Prevalence Of Obesity
A global surge in obesity rates alarms health experts. Recent statistics paint a worrying picture.
- Obesity affects adults and children alike.
- Modern lifestyle choices contribute significantly to this rise.
- Developed countries report higher obesity rates, echoing expanding waistlines worldwide.
This uptrend suggests urgent attention to preventive measures.
Defining Obesity: More Than A Number On A Scale
Defining obesity goes beyond simple weight metrics. Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common measure, yet it is not the sole indicator of obesity. Here’s a clearer breakdown:
| BMI Range | Category |
|---|---|
| < 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal weight |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30 or higher | Obese |
Obesity also includes factors such as fat distribution and metabolic health. These factors affect an individual’s risk for diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart conditions.
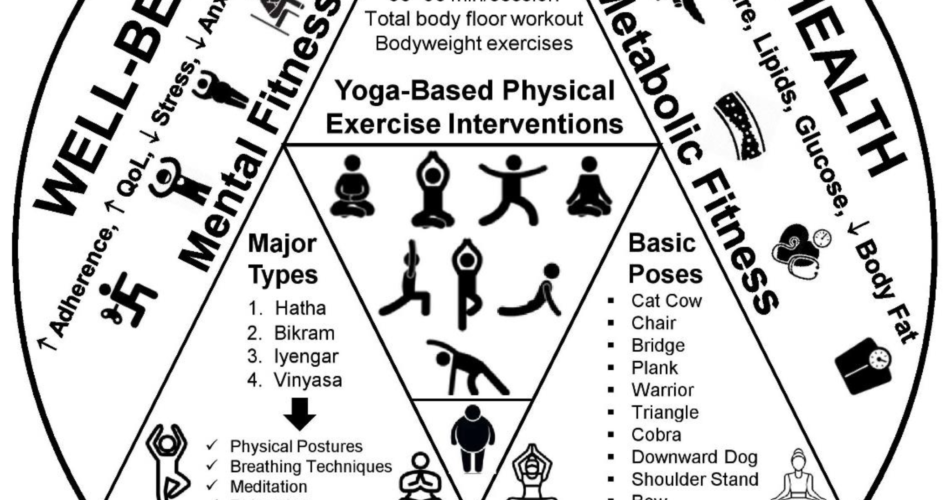
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Diving Into The Causes Of Obesity
Obesity is like a puzzle with many pieces that fit together. We need to look closely to see the whole picture. Let’s explore why some people become obese.
The Energy Imbalance Equation
Think of your body like a bank, where you save food as energy. If you save too much energy, you get heavier. Here’s why:
- Eating too much means more energy goes in.
- Being less active means less energy goes out.
This mismatch is called the energy imbalance equation. It can lead to weight gain over time.
Genetic Predispositions: How Dna Matters
Your DNA is like a recipe for your body. It can make obesity more likely for some people.
| DNA Factor | Effect on Obesity |
|---|---|
| Metabolism speed | Slower metabolism can store more fat. |
| Appetite control | DNA can make you feel hungry often. |
Lifestyle Factors: Diet And Physical Activity
Your daily choices also play a role. What you eat and how much you move are key pieces of the puzzle.
- Eat lots of sugary and fatty foods, gain more weight.
- Exercise less, don’t burn those extra calories.
A healthy plate and regular exercise help keep that energy bank balanced. It prevents too much weight gain.
The Multi-layered Impact Of Obesity
The Multi-layered Impact of Obesity spans across numerous aspects of life, profoundly affecting both individuals and societies. This weighty issue not only elevates health risks but also carries mental and economic repercussions.
Physical Health Risks: From Diabetes To Heart Disease
Obesity is no stranger to serious health threats.
- Diabetes: Carrying extra weight significantly increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes, a major health concern.
- Heart Disease: Obese individuals face a higher chance of heart problems, including hypertension and cardiac arrest.
- Joint Stress: Excessive weight can lead to osteoarthritis, as the added pressure strains the joints.
- Sleep Apnea: Obesity often results in sleep-disordered breathing, depriving the body of restful sleep.
Mental Health Considerations: Self-image And Depression
The impact of obesity extends into the realm of psychological health. A negative self-image is common among obese individuals. This can escalate into severe depression.
| Issues | Effects |
|---|---|
| Body Dissatisfaction | Reduced confidence and higher self-consciousness. |
| Social Stigma | Leads to social isolation and increased stress. |
| Depression | Might contribute to mood disorders and emotional distress. |
Societal Costs: Healthcare Burden And Productivity Losses
Obesity does not only strain an individual’s well-being but also weighs heavily on societal resources.
- Rising healthcare costs stem from the need to manage obesity-related health issues.
- Workplace productivity sees a decline as obesity can lead to increased absenteeism and lower job performance.
These losses are felt across economies, emphasizing the importance of addressing this global issue.

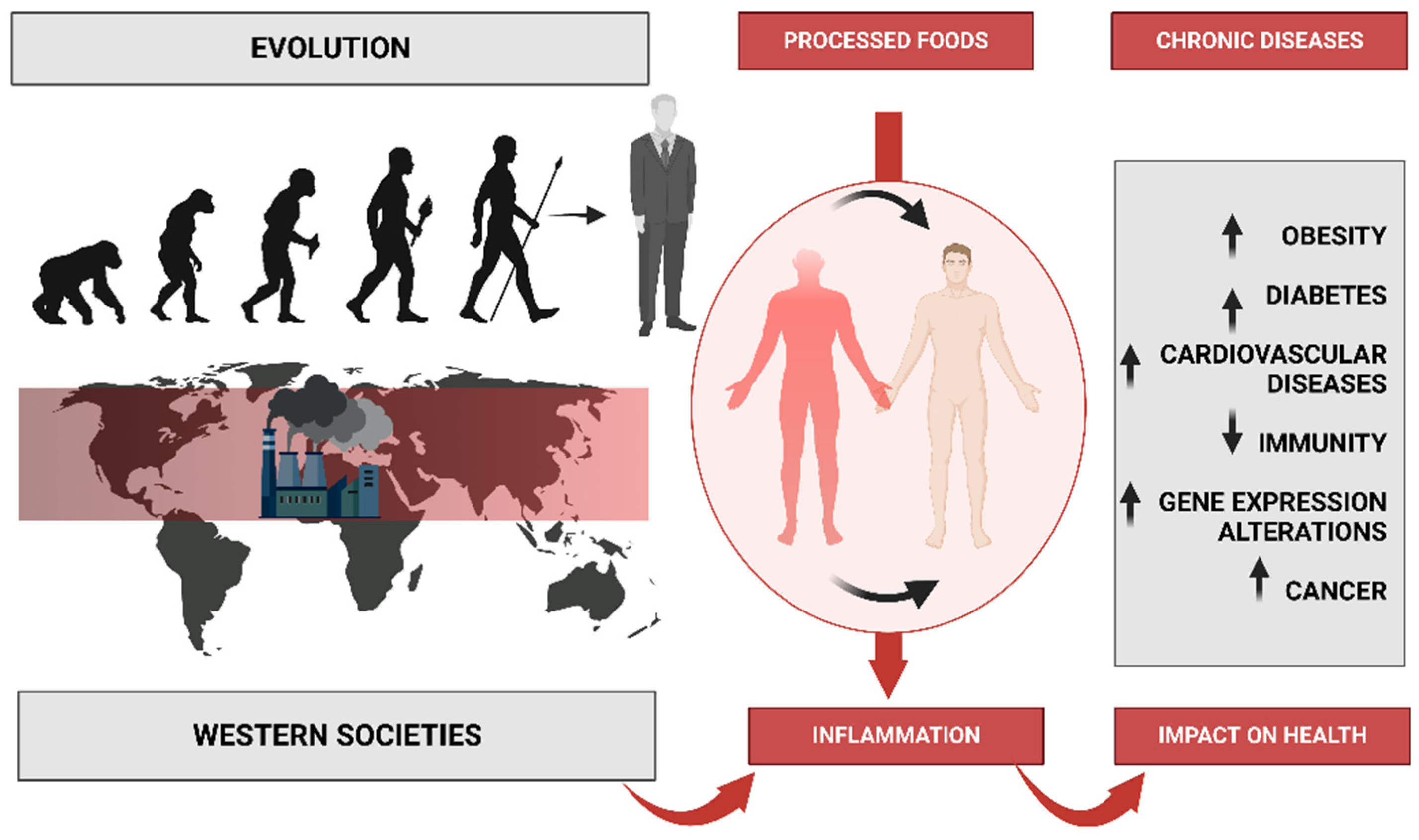
Credit: writology.com
Confronting Obesity: Prevention And Management
Tackling obesity demands a multifaceted approach, addressing both prevention and management. Understanding the deep-rooted causes and pervasive effects enables society to battle this modern-day health crisis effectively. Below, we dive into strategic avenues that play pivotal roles in confronting obesity.
Education And Awareness Strategies
Equipping individuals with knowledge is essential. Health education programs point to healthier lifestyles. Schools, workplaces, and communities benefit from structured nutritional information sessions. Interactive workshops and public health campaigns make this knowledge accessible.
- School-based initiatives teach children the value of balanced diets.
- Workshops address the importance of regular physical activity.
- Online platforms provide easy-to-understand dietary guides.
The Role Of Government And Policy
Government plays a critical role in shaping a healthier future. Legislation can control unhealthy food options and support physical education. Social policies encourage active living environments. Tax incentives and subsidies for healthy food options can shift consumption patterns.
| Policy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulating Food Advertising | Reduces consumption of unhealthy foods |
| Improving Urban Planning | Enhances access to recreational spaces |
| Fiscal Measures | Makes nutritious food more affordable |
Innovations In Medical Treatment And Support
Advancements in medicine provide hope in managing obesity. Bariatric surgery and weight management drugs offer solutions beyond conventional methods. These treatments come with support systems, like dietitian counseling and support groups, to ensure lasting lifestyle changes.
- Emerging drugs target metabolic pathways to curb obesity.
- Technology-based support tools, like apps, track diet and exercise.
- Behavioral therapy addresses psychological aspects of overeating.
Reflection On The Path Ahead
The journey to combat obesity is long and winding. Understanding the causes and effects has set the stage. Now, it’s time to look forward with a clear vision. The path ahead demands critical analysis and actionable changes. Lives depend on it. A healthier future is within reach. Let’s explore the current landscape and the road to transformation.
Critical Analysis Of Current Efforts
Many strategies have been employed to fight obesity. Despite efforts, obesity rates climb. Key initiatives exist, but they need refinement. Experts call for more effective measures. So, let’s delve into the effectiveness of these efforts.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Ads inform but rarely change habits.
- Nutrition Education: Schools teach healthy eating, yet access to nutrition varies.
- Regulation of Food Industries: Fast food marketing targets kids. Supervision remains lax.
- Community-Based Programs: Local initiatives show promise but lack widespread adoption.
Envisioning A Healthier Future: Changes Needed
The battle against obesity is not lost. It calls for renewed vigor and strategies. Visionaries suggest bold moves and societal shifts. The checklist below outlines essential changes.
- Amplify Education: Make nutrition knowledge universal. Ensure it’s practical.
- Improve Food Access: Healthy options must be affordable. They should be everywhere.
- Policy Tweaks: Stronger regulations on unhealthy food marketing can drive change.
- Involve All Stakeholders: Unite government, businesses, and communities for a common goal.
This fight requires unity and determination. We all play a role in forging this healthier path. The future can be bright and healthy. The time for action is now.
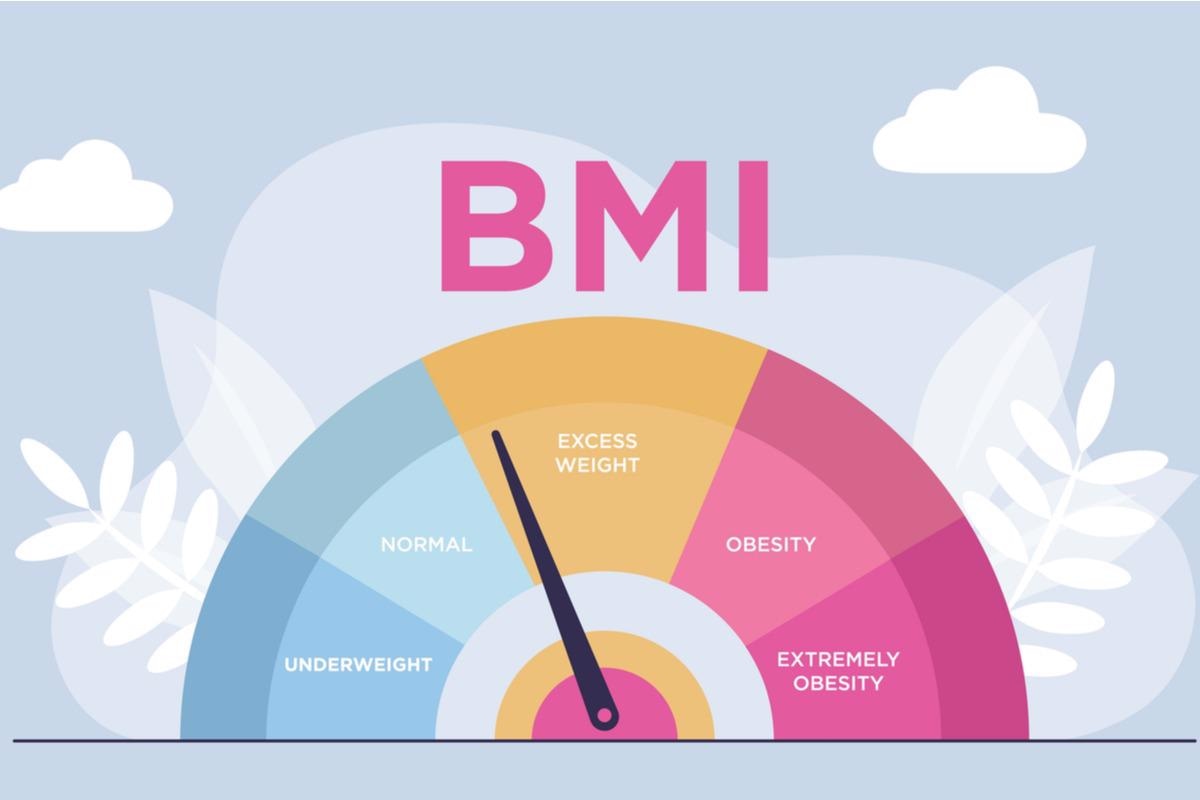
Credit: www.news-medical.net
Frequently Asked Questions On Causes And Effects Of Obesity Essay Conclusion
What Is A Good Conclusion For Obesity?
A good conclusion for obesity emphasizes adopting a healthy lifestyle, including balanced eating and regular exercise, to manage and prevent this complex health issue. It also highlights the importance of community support and proactive healthcare measures to address the obesity epidemic effectively.
What Is The Short Summary Of Obesity?
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excess body fat, significantly increasing health risks like heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. It often results from a combination of poor diet choices, lack of physical activity, and genetic factors.
What Is The Main Cause And Effect Of Obesity?
The primary cause of obesity is an energy imbalance between consumed and expended calories. Common effects include increased risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
What Is The Conclusion Of Child Obesity?
Child obesity typically results from a combination of poor diet, lack of physical activity, and genetic factors. It can lead to serious health issues like diabetes and heart disease. Effective prevention strategies include healthier eating habits and regular exercise.
Conclusion
Understanding the roots and repercussions of obesity is crucial for tackling this global health issue. By acknowledging the complex interplay between genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors, we can make informed decisions to improve individual and public health. Concrete steps towards balanced diets and regular exercise are key in preventing and managing obesity, ultimately leading to a healthier society.